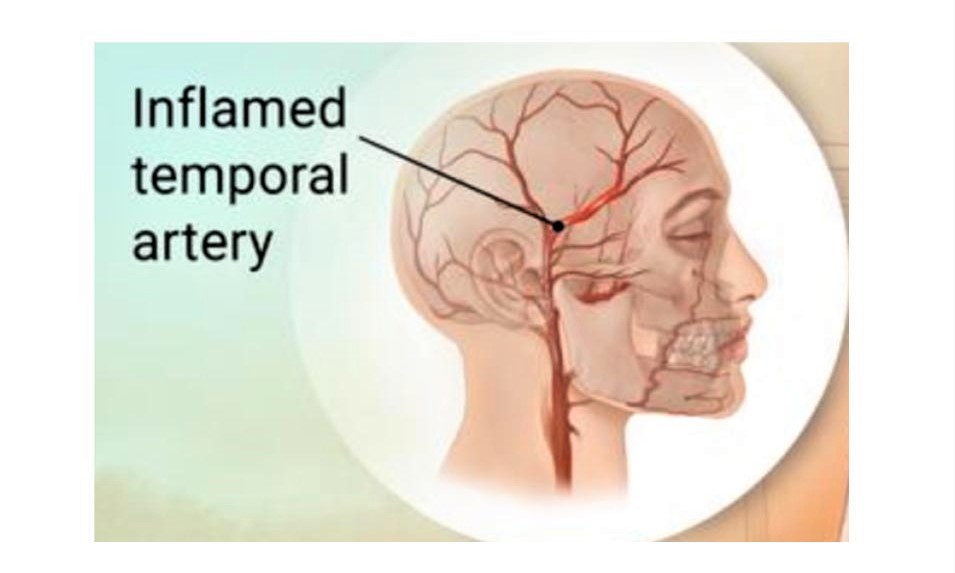
Giant cell arteritis is a condition that can cause headaches, trouble seeing, and jaw or arm pain. Also called GCA or temporal arteritis, it is a type of blood vessel inflammation that damages arteries. The most commonly affected arteries are those that start in the neck and travel into the head and scalp. It usually occurs in people aged 50 and older. Temporary loss of vision can be an early sign of GCA. Up to 10 percent of people with GCA can develop partial or complete blindness. If untreated, loss of vision can be permanent and/or can affect the other eye. Other symptoms of giant cell arteritis can include, new cough, fever, feeling tired, and weight loss.
If GCA is suspected, your provider will order blood tests for inflammation, ie, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or “sed rate”) and C-reactive protein (CRP). The diagnosis must be confirmed, either by biopsy of the temporal artery or with imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI, or PET scan). Giant cell arteritis is treated with medicines called steroids. Many people feel better after taking their first dose. But most people need to take steroids for 1 to 2 years. If you have headaches, especially with vision loss, please call The Manhattan Center for Headache and Neurology for an evaluation.
–Alice Wong, NP
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/giant-cell-arteritis
Visit Nervana Neurospa and Nervana Neurology & Wellness at our new Brooklyn location!
