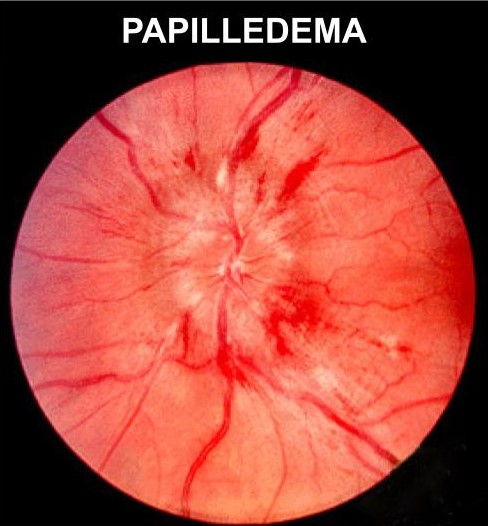
The term papilledema most properly describes optic disc edema, or inner eye edema, usually as a result of increased intracranial pressure. This increased pressure is transmitted to the optic nerve sheath and often causes serious consequences.
Common causes of increased intracranial pressure are intracranial mass lesion, cerebral edema (infection or severe TBI), increased cerebrospinal fluid production, and obstructive hydrocephalus.
Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure include headaches, usually positional, worsening with recumbency or in the morning. Associated symptoms can include visual disturbances (worsening eye vacuity, seeing double, loss of peripheral vision) and pulsatile machinery-like sounds in the inner ear.
The causes of papilledema often have serious consequences, therefore urgent brain MRI and lumbar puncture with opening pressure should be completed.
Additionally, serial measurement of visual acuity and fundoscopic exams should be used to assess the course of papilledema and response to treatment.
The Manhattan Center for Headache and Neurology has exceptional providers for further evaluation and potential treatment options.
By: Jordan Shankle, PA
